Eating Salad the Wrong Way? This Common Habit May Be Harming Your Health Without You Realising
- byPranay Jain
- 19 Feb, 2026
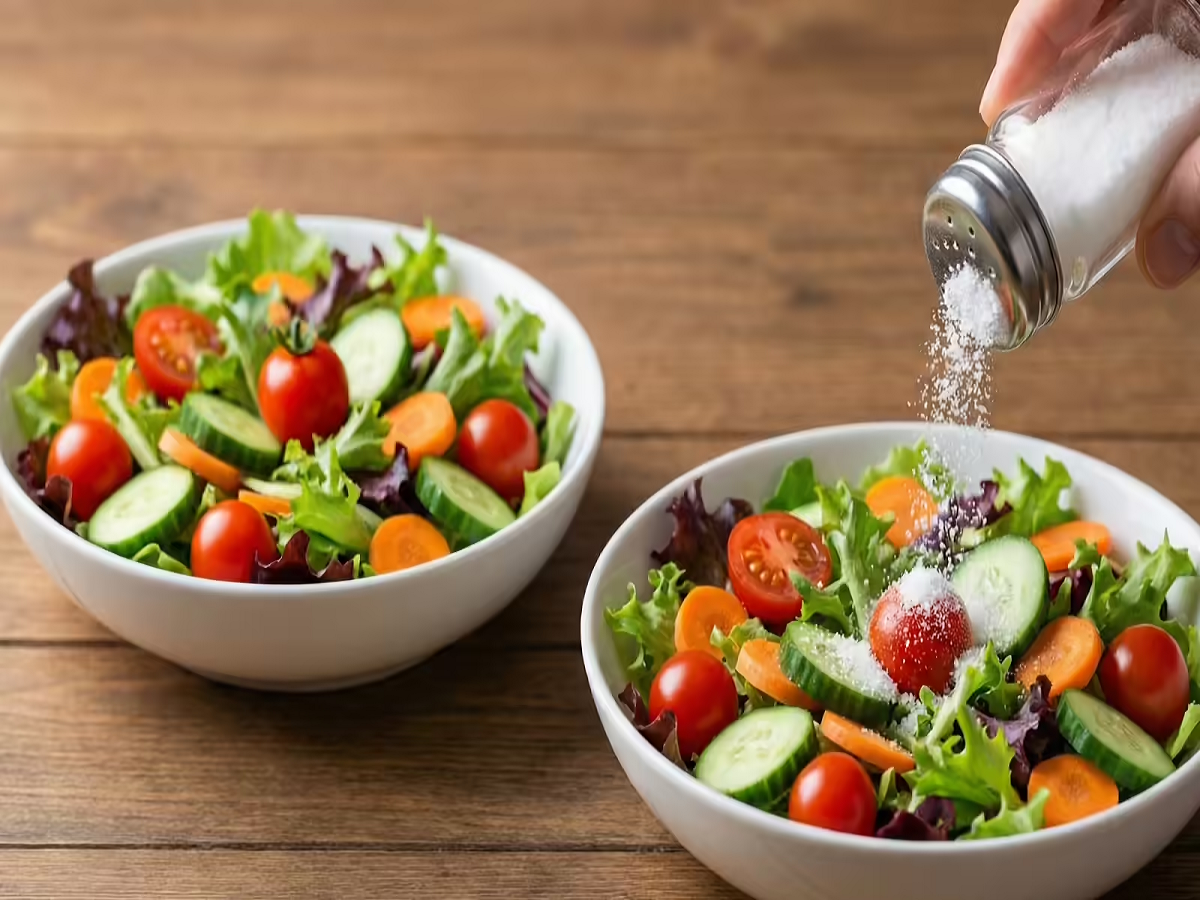

Salads are often considered one of the healthiest additions to a daily diet. Packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, salads help support digestion, immunity, weight management, and overall well-being. However, simply eating a salad does not automatically guarantee health benefits. The way you prepare and consume it matters just as much as the ingredients themselves.
One very common mistake many people make is adding salt directly to salads, especially while chopping vegetables or just before eating. While salt may enhance taste, this habit can quietly reduce the nutritional value of your salad and even lead to health problems over time.
Why Adding Salt to Salad Is a Bad Idea
Many people feel that raw vegetables taste bland without salt, so they sprinkle it generously to improve flavor. But this small habit can have long-term consequences, especially if salads are eaten daily.
When salt is added to fresh vegetables, it begins to draw out water from them through a process called osmosis. This not only makes the salad soggy but also leads to the loss of water-soluble nutrients, such as vitamin C and certain B vitamins. As a result, the salad becomes less nutritious than intended.
Salted Salads and Blood Pressure Risks
One of the biggest health concerns linked to adding salt to salads is its effect on blood pressure. Salt contains sodium, and excess sodium in the body is a well-known contributor to high blood pressure.
When sodium levels rise:
-
The body retains more water
-
Blood volume increases
-
Pressure on blood vessels rises
People who regularly consume salted salads may unknowingly exceed their daily sodium limit, especially if they already eat salty foods throughout the day. Over time, this can increase the risk of hypertension, headaches, dizziness, excessive sweating, and even heart-related issues.
If you are someone who eats salad daily to stay healthy, adding salt can actually cancel out some of those benefits.
Negative Impact on Bone Health
Adding salt to salad does not just affect blood pressure—it can also harm bone health. Excessive sodium intake is linked to increased calcium loss through urine. Calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth.
When calcium levels drop:
-
Bones may gradually weaken
-
Risk of fractures increases
-
Bone density can decrease over time
For people already at risk of osteoporosis or low bone density, regularly consuming high-salt foods—including salted salads—can worsen the condition. This makes avoiding added salt especially important for older adults and post-menopausal women.
How to Eat Salad the Right Way
If salt is not recommended, how can you make salads tasty without compromising health? The good news is that there are many healthier alternatives:
-
Use lemon juice or vinegar for natural tanginess
-
Add herbs and spices like black pepper, cumin powder, or oregano
-
Include healthy fats such as olive oil, nuts, or seeds to enhance flavor
-
Use natural ingredients like onions, tomatoes, or cucumbers for freshness
These options not only improve taste but also increase nutrient absorption and overall health benefits.
Who Should Be Extra Careful?
Certain people should be especially cautious about adding salt to salads:
-
Individuals with high blood pressure
-
People with kidney or heart conditions
-
Older adults
-
Those trying to lose weight or manage water retention
For these groups, reducing sodium intake is crucial, and salads should remain as natural as possible.
The Bottom Line
Salads are undeniably healthy—but only when eaten the right way. Adding salt may seem harmless, but over time it can affect blood pressure, weaken bones, and reduce the nutritional value of fresh vegetables.
If you truly want to enjoy the full benefits of salads, it’s best to avoid adding plain salt. Train your taste buds to appreciate natural flavors, and use healthier alternatives to enhance taste. Small dietary changes like this can make a big difference in long-term health.